Diabetes in children is a growing concern, affecting millions of families worldwide. This condition, which involves elevated blood sugar levels, can lead to serious health complications if not properly managed. Understanding diabetes in children, its symptoms, causes, and management strategies, is crucial for parents and caregivers to ensure the well-being of their children.
Understanding Diabetes in Children
Diabetes in children primarily manifests as either Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes, once considered rare in children, is now increasingly diagnosed due to rising rates of obesity and sedentary lifestyles.
Symptoms of Diabetes in Children
Recognizing the symptoms of diabetes in children early is vital for timely intervention and management. Common symptoms include:
- Increased Thirst and Urination: High blood sugar levels lead to increased urination, causing dehydration and excessive thirst.
- Extreme Hunger: Despite eating more than usual, children may experience persistent hunger due to the body’s inability to use glucose effectively.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Rapid weight loss, despite increased food intake, is a common symptom of Type 1 diabetes.
- Fatigue: Lack of insulin or insulin resistance can lead to constant fatigue and low energy levels.
- Irritability and Mood Changes: Sudden mood swings and irritability can be indicative of fluctuating blood sugar levels.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar can affect the eyes, leading to blurred vision.
- Slow-Healing Sores: Cuts and bruises that take longer to heal may signal underlying diabetes.
Causes of Diabetes in Children
The causes of diabetes in children vary between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
- Type 1 Diabetes: This form is believed to be caused by genetic and environmental factors. Family history plays a significant role, but the exact triggers are not fully understood. Viral infections and other environmental factors might contribute to the onset.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The primary causes include poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity. Genetic predisposition also plays a role, but lifestyle factors are significant contributors.
Diagnosis of Diabetes in Children
Early diagnosis of diabetes in children is crucial to prevent complications. The diagnostic process typically involves:
- Blood Tests: Tests such as the fasting blood sugar test, random blood sugar test, and HbA1c test measure blood glucose levels to diagnose diabetes.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: This test assesses the body’s ability to process glucose after ingesting a sugary drink.
- Autoantibody Tests: For Type 1 diabetes, tests to detect specific autoantibodies can confirm the autoimmune nature of the condition.
Managing Diabetes in Children
Effective management of diabetes in children requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and ongoing monitoring.
- Medical Treatment:
- Insulin Therapy: Children with Type 1 diabetes require insulin injections or an insulin pump to manage their blood sugar levels.
- Medications: For Type 2 diabetes, medications such as metformin may be prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity and control blood sugar levels.
- Dietary Changes:
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential.
- Carbohydrate Counting: Monitoring and managing carbohydrate intake helps in maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
- Regular Meals and Snacks: Consistent meal and snack times help in preventing blood sugar spikes and drops.
- Physical Activity:
- Regular Exercise: Encouraging children to engage in physical activities such as sports, biking, or swimming helps in managing weight and improving insulin sensitivity.
- Family Activities: Involving the whole family in physical activities can make exercise enjoyable and consistent.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels:
- Regular Testing: Frequent blood sugar testing helps in understanding how food, activity, and medications affect blood sugar levels.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): CGM devices provide real-time blood sugar readings, helping in better management.
Psychological and Emotional Support
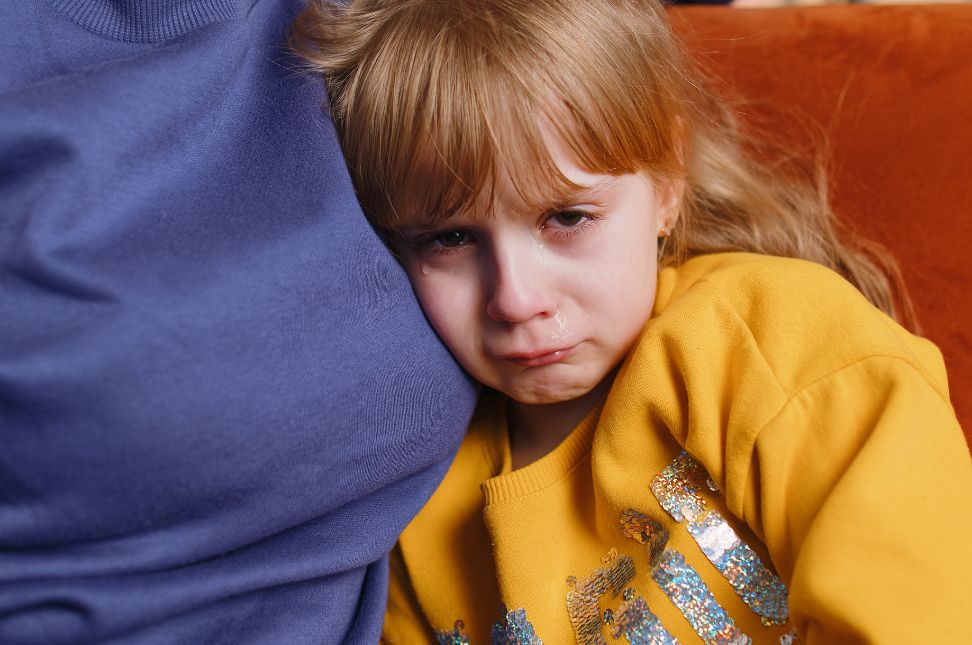

Living with diabetes in children can be challenging for both the child and the family. Providing emotional and psychological support is essential.
- Education and Counseling:
- Diabetes Education: Educating the child and family about diabetes management empowers them to handle the condition effectively.
- Counseling Services: Psychological counseling helps children cope with the emotional aspects of living with diabetes.
- Support Groups:
- Peer Support: Joining support groups where children and families share experiences can provide emotional comfort and practical tips.
- Family Support: Involving the entire family in the management plan ensures consistent support and understanding.
Preventing Complications
Preventing complications associated with diabetes in children requires diligent management and regular medical check-ups.
- Regular Health Check-ups:
- Eye Examinations: Regular eye exams help in detecting and managing diabetic retinopathy.
- Foot Care: Monitoring and caring for the feet prevent infections and complications.
- Kidney Function Tests: Regular tests to monitor kidney function are essential to prevent diabetic nephropathy.
- Vaccinations:
- Influenza and Pneumonia Vaccines: Vaccinations help in preventing infections that can complicate diabetes management.
- Influenza and Pneumonia Vaccines: Vaccinations help in preventing infections that can complicate diabetes management.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices:
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking exacerbates diabetes complications and should be avoided.
- Healthy Habits: Encouraging a healthy lifestyle, including proper sleep and stress management, supports overall well-being.
Conclusion
Diabetes in children is a serious condition that requires comprehensive management and support. Early diagnosis, effective treatment, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support are crucial for managing diabetes and preventing complications. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and management strategies, parents and caregivers can help children with diabetes lead healthy, fulfilling lives.